test to differentiate testicular torsion from epididymitis|epididymo orchitis guidelines : sourcing Testicular isotope scanning can differentiate epididymitis, which results in “hot spots” caused by increased perfusion near the affected testicle, from testicular torsion, which results in . Resultado da The purpose of Emupedia (Emulation Encyclopedia) is to serve as a nonprofit meta-resource hub and community for those interested mainly in video game preservation and computer history which aims to digitally collect, archive and preserve games and software to make them available online accessible by .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web22 de abr. de 2022 · Baixe a última versão do Premiere Play para Android . Uoldown e os cookies: a gente usa cookies para personalizar anúncios e melhorar a sua experiência no site. Ao continuar navegando, você concorda com a nossa Política de Privacidade.. continuar e fechar
testicular torsion vs orchitis
Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of .Our study demonstrates that scrotal scintigraphy is a simple, accurate, and effective functional imaging technique that can differentiate acute epididymitis from testicular torsion in selected .
testicular torsion vs epididymo orchitis
Prehn's sign (named after urologist Douglas T. Prehn) is a medical diagnostic indicator that was once believed to help determine whether the presenting testicular pain is caused by acute epididymitis or from testicular torsion. Although elevation of the scrotum when differentiating epididymitis from testicular torsion is of clinical value, Prehn's sign has been shown to be inferior to Doppler ultrasound to rule out testicular torsion.
A study by Asgari et al suggests that C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) may be useful in differentiating epididymitis from testicular torsion. In .
Testicular isotope scanning can differentiate epididymitis, which results in “hot spots” caused by increased perfusion near the affected testicle, from testicular torsion, which results in .
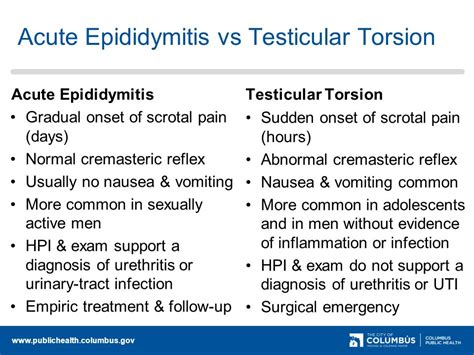
This presentation helps differentiate epididymitis and orchitis from testicular torsion, which is a surgical emergency. Typical physical findings include a swollen, tender epididymis or.
Since the presentations of epididymitis and testicular torsion overlap, it is sometimes difficult to rapidly make the correct diagnosis. Early genitourinary consultation is appropriate in this setting. Epididymitis is managed medically, whereas testicular torsion is a surgical emergency. This activity reviews the presentation, evaluation, and management of .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is .
testicular torsion vs epididymitis ultrasound
Ultrasound and nuclear scans help differentiate testicular torsion from epididymitis. CT and MRI scans are used occasionally to help determine and differentiate between many conditions that can cause some symptoms similar .A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes). Prehn’s test is used to differentiate testicular pain caused by acute epididymitis and testicular torsion. The test involves elevating the testes to assess the impact on testicular pain. A reduction in testicular pain is .Investigation and treatment. Colour Doppler sonography is indicated in equivocal cases, but has operator-dependent factors that can cause variances in sensitivity (86–100%) and specificity (95–100%). 3,8–10 Importantly, a normal .
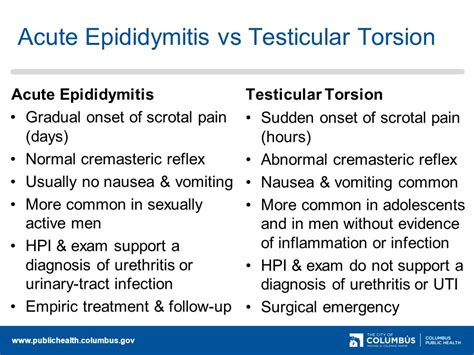
Doctors suspect epididymitis or epididymo-orchitis based on a physical examination. They'll usually also do: A urine test to look for infection. Sometimes, ultrasound, to be sure that you don't have a twisted testicle (testicular torsion) Unlike epididymitis, which typically has a gradual onset of symptoms, testicular torsion presents with sudden, severe scrotal pain and swelling, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.22,23 On physical examination, the affected testicle may be high-riding and sit abnormally, and the cremasteric reflex (a reflex triggered by stimulating the .The appendix testis is a small appendage of normal tissue that is usually located on the upper portion of the testis. The appendix epididymis is a small appendage on the top of the epididymis (a tube-shaped structure connected to the testicle). Torsion of an .
To differentiate epididymitis from testicular torsion, the doctor may test the cremasteric reflex (in which the testicle rises when the inner thigh is stroked). A positive cremasteric reflex generally excludes testicular torsion as a cause. There would also be a positive Prehn sign, in which pain persists even when the scrotum is lifted.
Testicular torsion and acute epididymitis are a major subject and can be identified in the majority of cases by medical history taking, clinical examination and scrotal ultrasound. Suspicion of testicular torsion is an indication for urgent surgical exploration.
Imaging of the scrotum in the setting of acute symptoms such as pain or swelling is commonly performed emergently to differentiate between patients who require immediate surgery and those who do not. . A retrospective review of pediatric patients with epididymitis, testicular torsion, and torsion of testicular appendages. Pediatrics. 1998 Jul . The authors of a retrospective review of 204 boys with torsion, torsion of the appendix testis, or epididymitis/orchitis found no difference in presenting symptoms or historical features other . The area is painful and tender. There can be enlargement of the testis and is hot, red and swollen. Patients can experience lower urinary tract symptoms such as frequency and dysuria. Uncommon signs are urethral discharge, fluctuant swelling and fever. A useful sign to differentiate between testicular torsion and epididymitis is the cremasteric . To differentiate between testicular torsion and epididymitis, a healthcare professional may perform a physical examination, order laboratory tests, and conduct imaging studies such as an ultrasound. Treatment for epididymitis typically involves a course of antibiotics to eliminate the underlying infection.
Causes of testicular torsion. There are two mechanisms for testicular torsion, intravaginal and extravaginal. Intravaginal. Intravaginal torsion occurs due to a lack of fixation of the posterolateral section of the testis to the inner wall of the scrotum.. This occurs due to a higher than usual attachment point of the tunica vaginalis to the testis and epididymis within the sac. More common than testicular cancer is epididymitis, which is inflammation of the epididymis, a tubular structure next to the testicle where sperm mature. About 600,000 men get it each year, most .
Question 1 Describe symptoms, historical features and US findings in • Testicular torsion • Epididymoorchitis , epididymitis Ultrasound is an essential tool in differentiating between the different causes of testicular pain however ultrasound alone cannot exclude torsion. Initially ultrasound findings in testicular torsion may be unremarkable and then become .For men with severe unilateral pain with sudden onset, those whose test results do not support a diagnosis of urethritis or urinary tract infection, or for whom diagnosis of acute epididymitis is questionable, immediate referral to a urologist for evaluation for testicular torsion is vital because testicular viability might be compromised.Testicular torsion. Testicular tumor. Testicular cancer. What is the difference between epididymitis and orchitis? Epididymitis refers to inflammation of the tube at the back of your testicle. Orchitis is when your testicle itself swells. These conditions sometimes occur at the same time. When this happens, healthcare providers call it . The Impact of Testicular Torsion on Testicular Function. World J Mens Health. 2020 Jul. 38 (3):298-307. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. . Schick MA, Sternard BT. Testicular Torsion. 2024 Jan. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. . Lacy A, Smith A, Koyfman A, Long B. High risk and low prevalence diseases: Testicular torsion. Am J Emerg Med. 2023 Apr. 66:98-104.
vq40 compression test
Soybean Test 2 . 52 terms. taypip04. Preview. Lab3 WS patient prep& endotracheal intubation . How to differentiate testicular torsion from acute epididymitis/orchitis on doppler U/S? . How to differentiate testicular torsion from acute epididymitis/orchitis on nuclear testicular scan? 1. testicular torsion: DECREASED radiotracer activity 2 .
Answer B - ultrasound If your client has a rapid onset of unilateral scrotal pain radiating up to the groin and flank and you are trying to differentiate between epididymitis and testicular torsion, an ultrasound test is useful to determine whether the swelling is in the testis or the epididymis and should be your first choice. Initially, before the swelling has reached its peak, a physical . Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18. Previous testicular torsion. If you've had testicular pain that went away without treatment (intermittent torsion and detorsion), it's likely to occur again. The more frequent the bouts of pain, the higher the risk of testicular damage. Family history of testicular torsion.
Ultrasound and nuclear scans help differentiate testicular torsion from epididymitis. CT and MRI scans are used occasionally to help determine and differentiate between many conditions that can cause some symptoms similar to epididymitis (for example, cysts, hydrocele formation (fluid filled area), hernias, cancerous tissue, or the extent of .
testicular torsion vs epididymitis test
Testicular isotope scanning can differentiate epididymitis, which results in “hot spots” caused by increased perfusion near the affected testicle, from testicular torsion, which results in .Objective: To identify the signs that can help to differentiate torsion of the appendix testis (AT) and epididymitis and to establish the incidence of the various pathologic entities in boys with an acute scrotum. Materials and methods: A retrospective study was performed of the data from all boys treated at our institute from January 2008 to January 2012 for the diagnosis of an "acute .
testicular torsion treatment
Diagnosis and Management of Testicular Torsion, Torsion of the Appendix Testis, and Epididymitis Shan Yin, MD, MPH,⁎ Jennifer L. Trainor, MD† Because acute scrotal pain, swelling, and/or inflammation are a potential surgicalScrotal and testicular masses can be broadly categorized into painful conditions, which include testicular torsion, torsion of the testicular appendage, and epididymitis, and painless conditions .Introduction. Epididymitis and testicular torsion are two conditions that affect the male reproductive system. While both can cause pain and discomfort in the scrotum, they have different causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
prehn sign vs cremasteric reflex
24 de fev. de 2023 · The Consultant: With Christoph Waltz, Nat Wolff, Brittany O'Grady, Aimee Carrero. Follows a relationship between employee and boss, asking how far we .
test to differentiate testicular torsion from epididymitis|epididymo orchitis guidelines